This week we focused on population and variance. Population is a localized community of animals of the same species that breed with each other. Populations evolve through natural selection as the fittest individuals are selected to survive and reproduce and pass on their genes to their offspring. The genetic makeup of the population will change over time as favorable traits are passed down and increase in frequency.
In order for this to work, you need to have variance in the population. Variance is the raw material for natural selection. If the population was completely uniform then there would be no way of it to evolve because all individuals would be equally fit for the environment. Because of variety within the population, certain individuals will have a greater reproductive success.
Where does variance come from? It comes from mutations and sex. Mutations happen randomly and are changes of DNA in certain individuals. Some mutations can increase an individuals likeliness to survive, while other mutations can have the opposite effect and are not usually passed down. Sex is the recombination of genes. Each offspring will have a different genetic code than either parent so it is a way to mix the genes and have new arrangements of DNA every generation.
Changes in allele frequency are also caused by gene flow and genetic drift. Gene flow is the movement of individuals in and out of a population which affect the gene pool. This reduced differences between populations. For example, humans are having a greater gene flow as technology and transportation has made traveling easier. It has been predicted that in the future, humans will be much more similar to each other in appearance.

This photo if famous for representing what a future American citizen will look like as more people from different races, ethnicities and locations reproduce more and more.
Genetic drift is an effect of chance events such as bottleneck and flounder events. These events usually result in the loss of alleles in the gene pool which reduces variation and adaptability.

We also learned about the Hardy-Weinberg equations which represent a hypothetical population that does not have natural selection. This could never happen in reality but it serves as a useful tool to measure what type of evolution is happening in different populations.

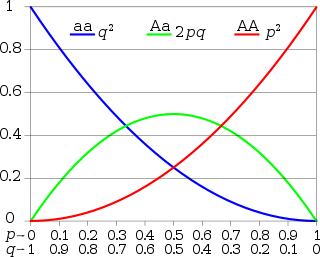



 It included these
It included these 
